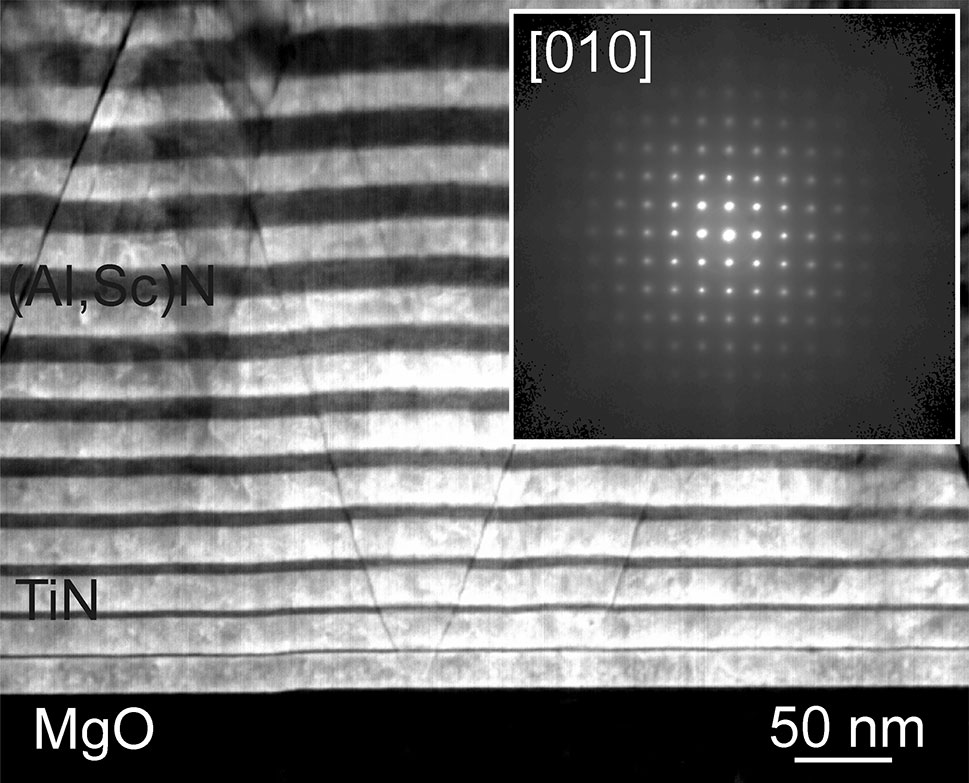
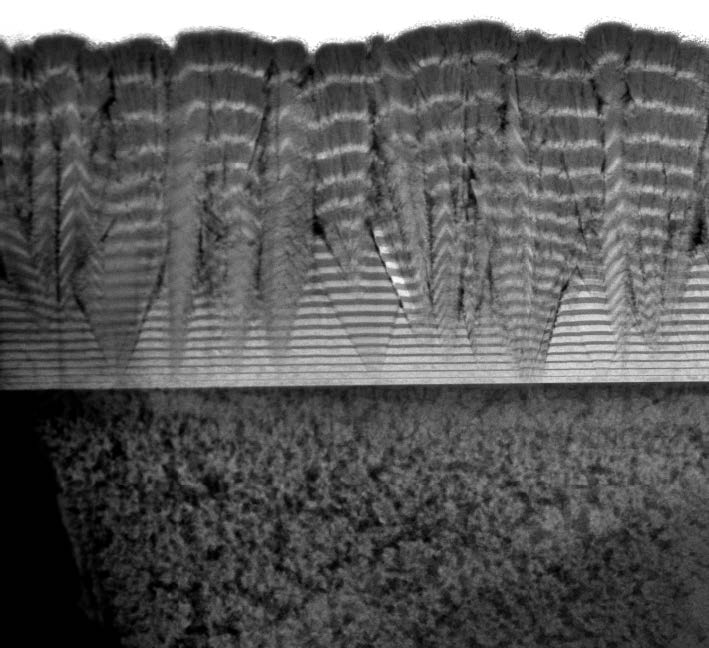
Ni50Ti50 nm-sized amorphous particles are prepared using inert-gas condensation followed by in situ compaction. Elemental segregation of Ni and Ti is observed in the consolidated nanostructured material Amorphous, nearly pure Nickel (96%) nanophases form within the amorphous Ni50Ti50 alloy. Combining atom probe tomography and scanning transmission electron microscopy with computer modelling, we explore the formation process of such amorphous nanophase ...
Read more