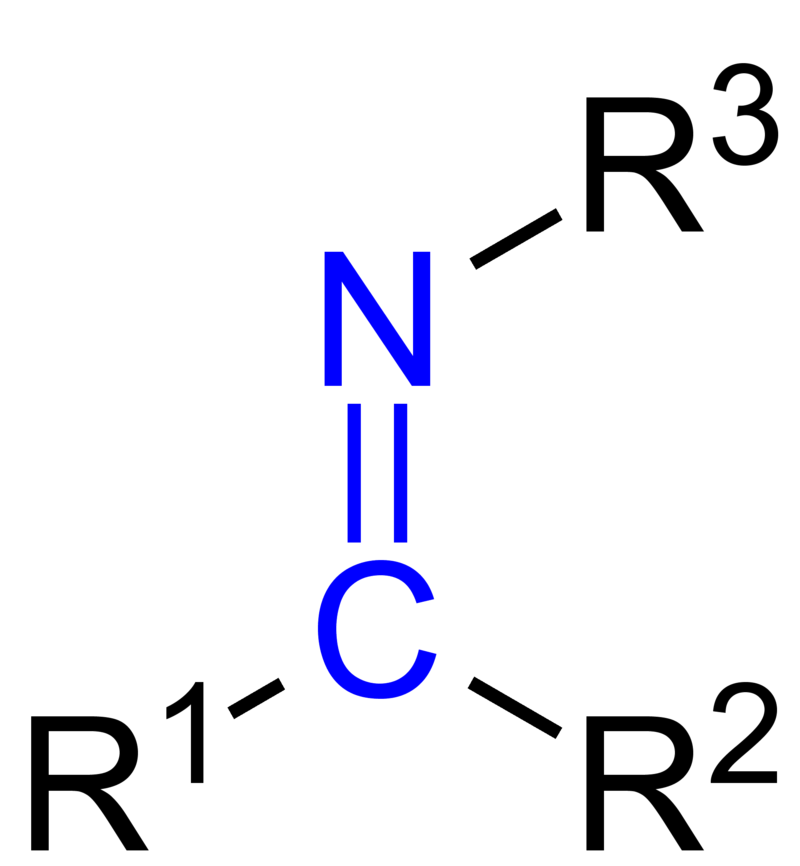
A series of new Iron(II) Schiff base amino acid complexes derived from the condensation of amino acid and sodium 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde-5-sulfonate have been synthesized. The complexes were characterized by elemental, electronic, IR spectral analyses and conductance measurements. The stability and solubility of the prepared complexes were determined. Two spectral methods used to determine the stoichiometry of the prepared complexes which exhibited ...
Read more