Background: Variable protocols for the management of cleft lip and/or palate (CLP) patients are
currently used. However, to our knowledge, there are no previously published data about cleft
management and practice in Egypt. Materials and Methods: One-hundred questionnaires were
distributed to cleft surgeons attending the annual meeting of the Egyptian Society of Plastic and
Reconstructive Surgeons in March 2016 to investigate timing, techniques and complications of
cleft surgery. Seventy-two colleagues returned the questionnaire, and the data were analysed
using Microsoft Excel software. Results: The majority of cleft lip cases are repaired between
3 and 6 months. Millard and Tennison repairs for unilateral cleft lip, while Millard and Manchester
techniques for bilateral cleft lip are the most commonly performed. Cleft palate is usually repaired
between 9 and 12 months with the two-flap push-back technique being the most commonly
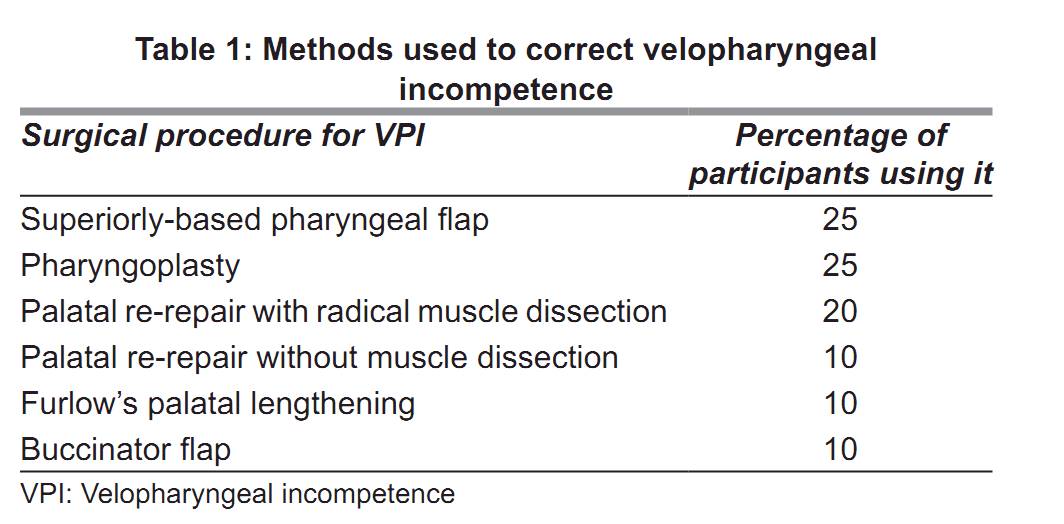
used. The average palatal fistula rate is 20%. Pharyngeal flap is the method of choice to correct
velopharyngeal incompetence. Polyglactin 910 is the most commonly used suture material in cleft
surgery in the country. Multidisciplinary cleft management is reported only by 16.5% of participants.
Conclusion: Management of CLP in Egypt is mainly dependent on personal preference, not on
constitutional protocols. There is a lack of multidisciplinary approach and patients’ registration
systems in the majority of centres. The establishment of cleft teams from the concerned medical
specialties is highly recommended for a more efficient care of cleft patients.