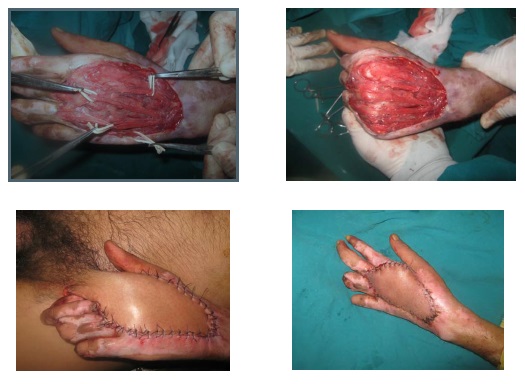
Purpose: A large number of hand injuries is presented to Sohag university casualty unite which attract our attention to the need to establish a specialized services to hand trauma through which, we can assess the prevalence and pattern of hand trauma in one year period in the casualty unit of Sohag University hospital and evaluate different techniques of reconstruction of soft tissue injuries and defects involving the hand.
Patients and methods: A retrospective analysis of patients with different patterns of hand trauma presented to the plastic surgery department in a 1 year duration (from August 2008 to July 2009) of 745 cases.
Results: A total of 745 cases of hand trauma were recorded; 553 males (74%) and 192 females (26%) were involved. The majority of cases in the study (47 %) were in the age group of < 15 years. The most common mode of trauma was the blunt crushing injuries (motor car accident, hummer trauma and door trapping trauma) which represents (49 %) of cases, followed by sharp object trauma which represents (30 %) of cases and lastly hand burns which represents (21%) of cases. Sex distribution showed a male to female ratio of 2.9:1.
Conclusions: Prompt and proper management of hand trauma by specialized hand surgeon has a great influence on the outcome and decrease incidence of complications. This includes special hand surgery team, well arranged operating room, general protocol of management, good post operative follow up and availability of physiotherapy team. Careful management will allow for a faster and complete recovery.