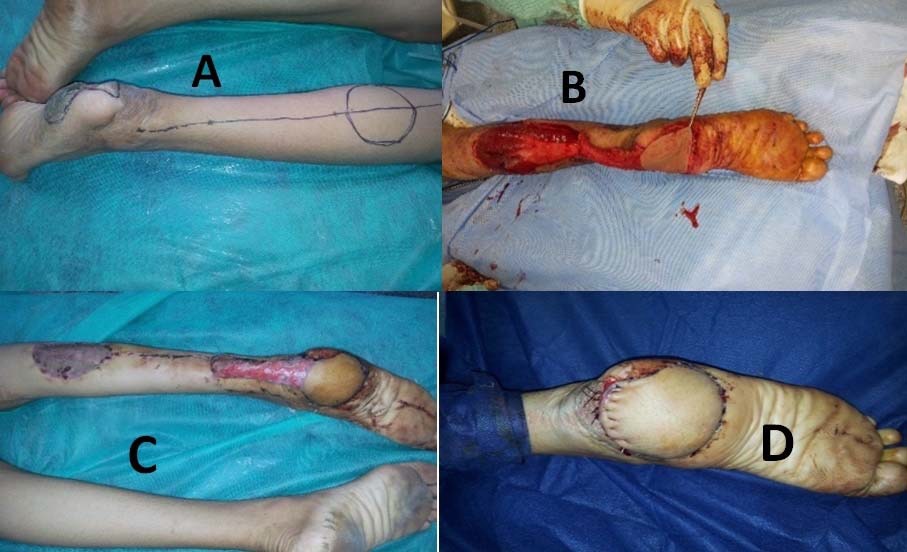
Background: Foot trauma may have a major influence on life style in the form of chronic pain, ulcers and diminished function. These potential complications can be minimized by appropriate management of foot soft tissue injuries. Proper wound debridement and meticulous hemostasis are essential. The ultimate goal of reconstruction is to close the wound and to provide for bipedal ambulation.
Methods: During the period from January 2010 to December 2014, 164 patients with soft tissue defects in the foot underwent reconstruction in the plastic surgery department of Sohag university hospital. Reconstructive method was chosen according to the local finding of each defect as well as the general clinical status of the patient. Skin grafts, fasciocutaneous and myocutaneous flaps, either pedicled or free, were utilized. The minimal post-operative follow up was 6 months.
Results: 169 foot soft tissue defects in 164 consecutive patients were reconstructed. The etiology was acute trauma in 152 and chronic trauma in 12 cases. Modalities of reconstruction used were: 72 skin grafts, 51 cross-leg flaps, 15 flap repositioning and direct closure, 12 local flaps, 9 sural flaps, 5 dorsalis pedis flaps, 4 free flaps and 1 medial planter flap. Overall complication rate was 12%.
Conclusion: Reconstruction of the foot should start by the simplest procedure that can accomplish the desired anatomical and functional outcome. Although microsurgical progress has improved and changed the quality of lower limb reconstruction, pedicled flaps remain good solution in selected cases.