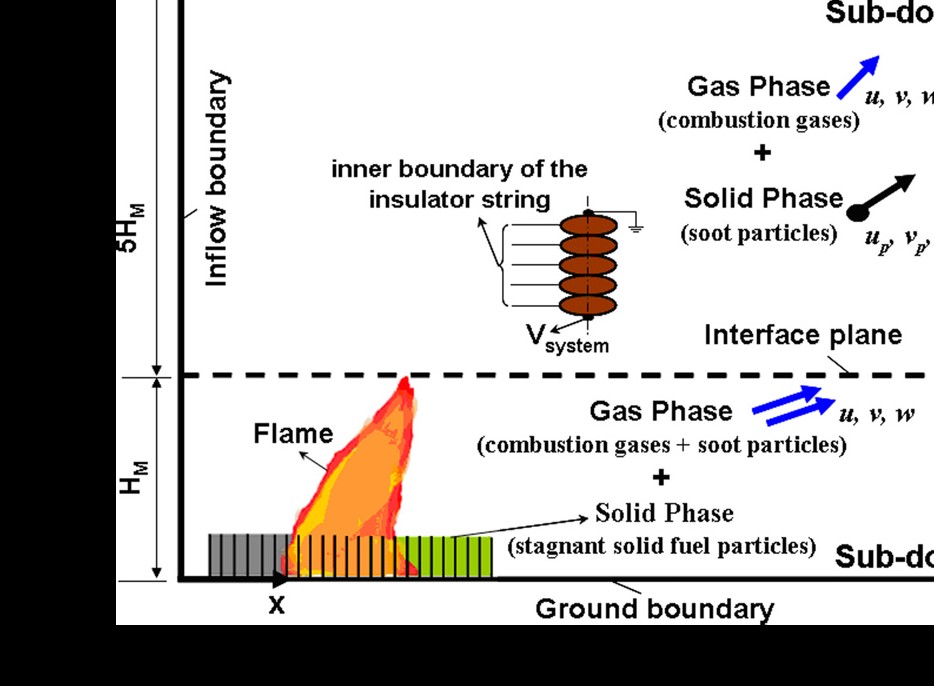
This paper presents a mathematical integrated model that simulates the coupled events causing flashover
due to the deposition of soot particles on suspension insulators of high voltage transmission lines (HVTL).
The model considers non-steady three-dimensional multi-phase flow of agricultural fire producing the
soot particles. In addition, the model describes in detail the mechanism of the soot deposition combined
with the developing of the electric field. The model equations are simultaneously solved using an iterative
finite-volume numerical technique together with the indirect boundary element and charge simulation
methods. The model validity and accuracy are verified through the discussion of the results for a representative case study of a 15 kV cap-and-pin insulator string. The discussion includes a comparison of the present numerical predictions for characteristics of the deposited soot layer, electric field distribution,
and characteristics of flashover occurrence, with the available results in the literature.