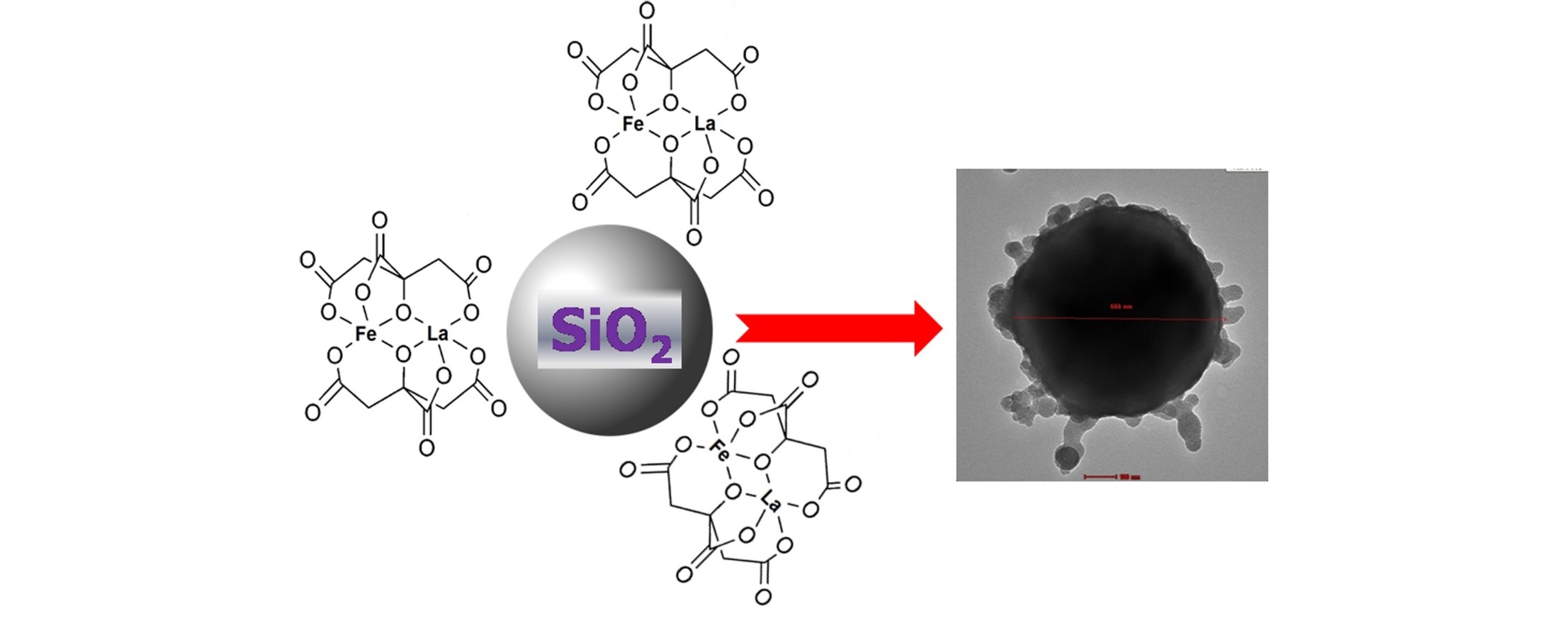
A series of 10, 20 and 30% (w/w) La2O3-Fe2O3/silica composites were synthesized by mixing of La-Fe citrate complex gels with spherical silica sols. This was followed by calcination of the formed xerogel at 550 °C and 750 °C for 3 h. The materials were characterized by XRD, simultaneous thermal analyses (TGA-DTA), FTIR, N2 gas adsorption/desorption isotherms at ⿿196 °C, and TEM techniques. Results indicated complete decomposition of the precursor complex upon calcination and development of porous composites with high surface area. However, processing of the La-Fe citrate complex gel or the silica precursors without mixing led to formation of LaFeO3 perovskite oxide type and silica with very low surface area amounting to 4 and 11 m2/g, respectively. Thus the process led to the formation of nanosized amorphous-like LaFeO3 phase (as a shell) on the surface of the spherical silica particles (core). The enhancement of surface area and porosity of the composites was correlated to the dispersion of La-Fe precursor on the surface of silica sol. The method can be generalized for other mixed oxides.