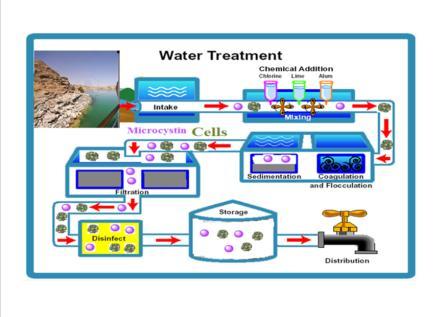
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) have increased throughout the world's coastal oceans during the last century mostly due to water eutrophication and climate change. These blooms are often accompanied by extreme extensive negative impacts to fisheries, coastal resources, public health and local economies. However, limited studies have reported HAB events in Red Sea coastal waters. This article reviews potentially harmful microalgae ...
إقراء المزيد