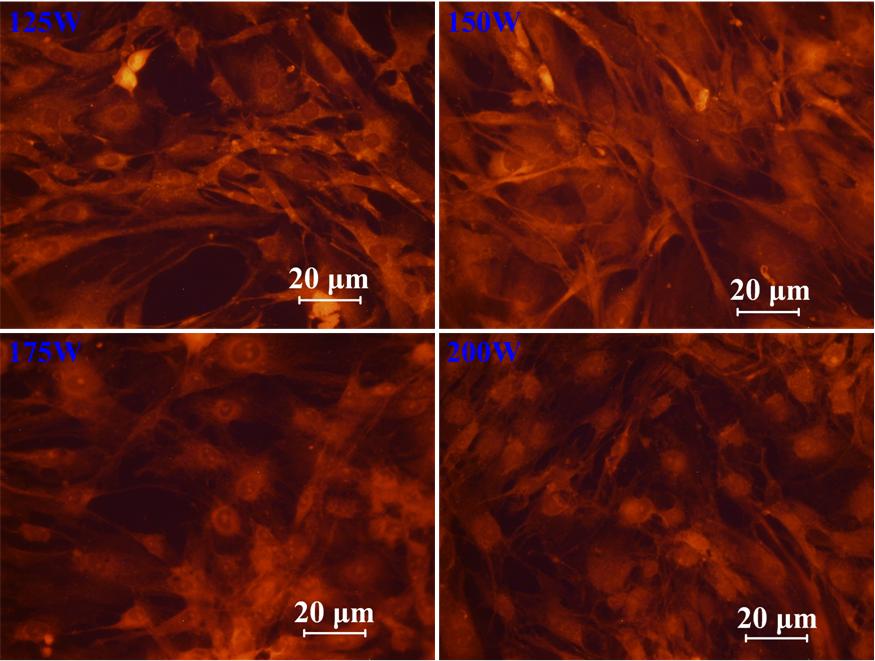
The Dc. pulsed magnetron sputtering was employed to deposit Ti-Zr-N thin film on AISI 316 substrates. All the plasma parameters were kept to be constant except the plasma-processing power which was varied from 125 W to 250 W. The structure, tribological, electrochemical and biocompatibility properties of Ti-Zr-N films have been investigated. X-ray patterns confirmed the formation of solid solution phase of Ti-Zr-N with different orientations. The results depicted that, the microhardness of Ti-Zr-N film increases with increasing the plasma-processing power to reach a maximum value of approximately 1050 HV0.015 at 200 W. Moreover, the tribological properties of the coated AISI 316 with Ti-Zr-N were found to be superior compared with the uncoated sample. The wear rate of the coated sample at 225 W has a value of nearly 0.0034 mm3/Nm which is very low in comparison with AISI 316 substrate that has a value of 0.137 mm3/Nm. The biological properties of the examined samples were evaluated by investigating the proliferation of MC3T3-E1 osteoblast cells on the surfaces. The proliferation rate of the osteoblast cells was enhanced on Ti-Zr-N films prepared at low plasma power. It has been demonstrated that the surface roughness and surface energy besides the surface chemical compositions affect the tribo-mechanical and biocompatibility features of Ti-Zr-N surfaces.