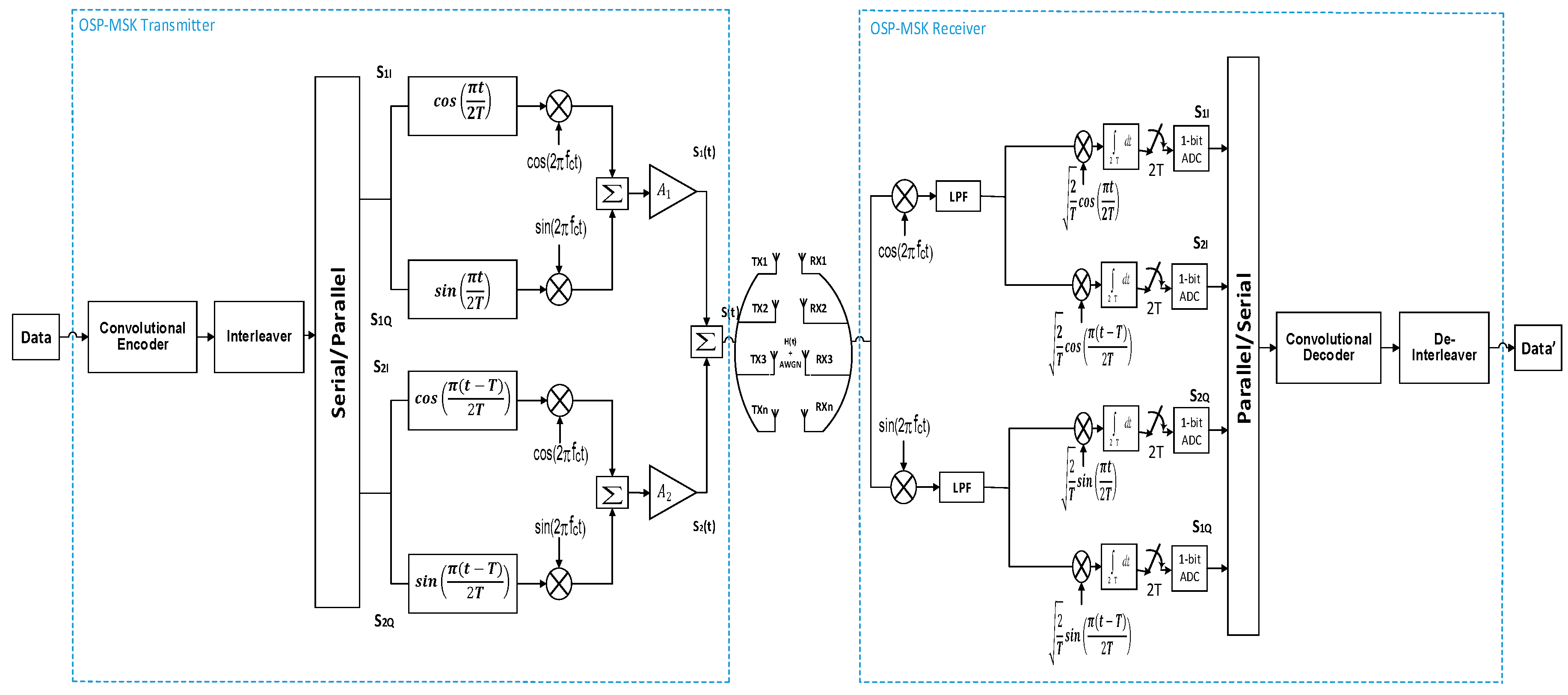
Due to the Internet of Things (IoT) requirements for a high-density network with low-cost and low-power physical (PHY) layer design, the low-power budget transceiver systems have drawn momentous attention lately owing to their superior performance enhancement in both energy efficiency and hardware complexity reduction. As the power budget of the classical transceivers is envisioned by using inefficient linear power amplifiers (PAs) at the transmitter (TX) side and by applying high-resolution analog to digital converters (ADCs) at the receiver (RX) side, the transceiver architectures with low-cost PHY layer design (i.e., nonlinear PA at the TX and one-bit ADC at the RX) are mandated to cope with the vast IoT applications. Therefore, in this paper, we propose the orthogonal shaping pulses minimum shift keying (OSP-MSK) as a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) modulation/demodulation scheme in order to design the low-cost transceiver architectures associated with the IoT devices. The OSP-MSK fulfills a low-power budget by using constant envelope modulation (CEM) techniques at the TX side, and by applying a low-resolution one-bit ADC at the RX side. Furthermore, the OSP-MSK provides a higher spectral efficiency compared to the recently introduced MIMO-CEM with the one-bit ADC. In this context, the orthogonality between the in-phase and quadrature-phase components of the OSP are exploited to increase the number of transmitted bits per symbol (bps) without the need for extra bandwidth. The performance of the proposed scheme is investigated analytically and via Monte Carlo simulations. For the mathematical analysis, we derive closed-form expressions for assessing the average bit error rate (ABER) performance of the OSP-MSK modulation in conjunction with Rayleigh and Nakagami-m fading channels. Moreover, a closed-form expression for evaluating the power spectral density (PSD) of the proposed scheme is obtained as well. The simulation results corroborate the potency of the conducted analysis by revealing a high consistency with the obtained analytical formulas.