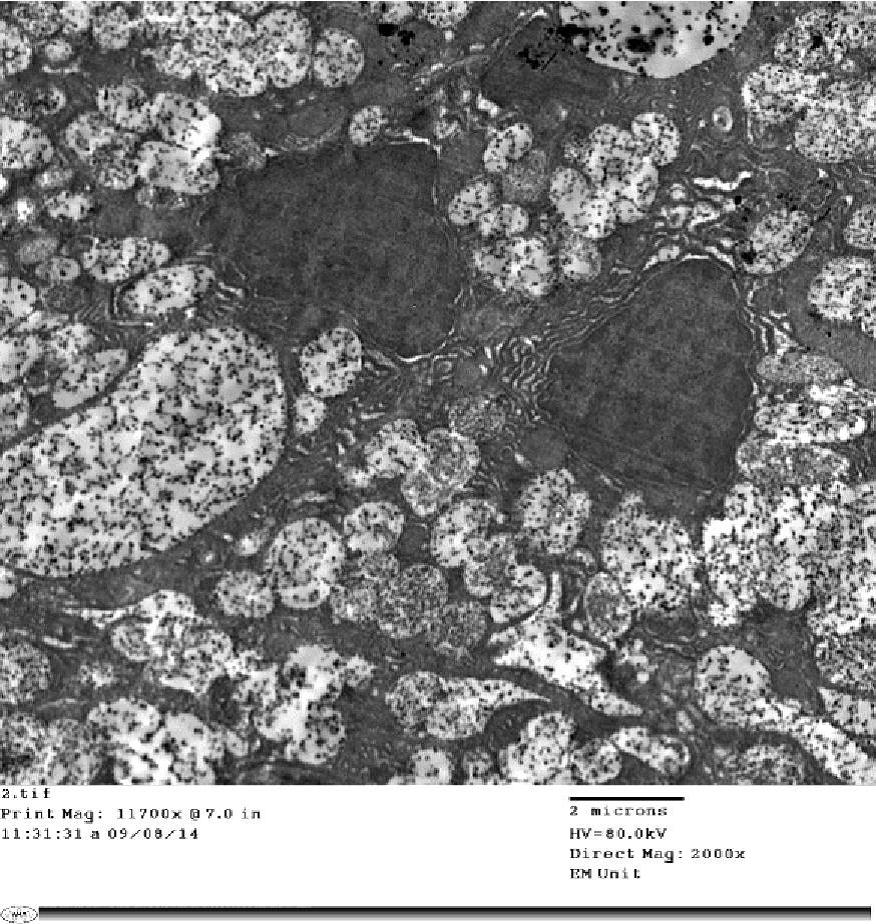
INTRODUCTION Aging represents a major risk for vascular diseases. Diseases of the aorta exert serious effects on the heart. AIM This study aimed to detect the histological changes of the aged aorta, understand their underlying mechanisms, and help in the development of prophylactic and treatment measures. MATERIALS AND METHODS Ten adult and 10 aged male albino rats were used. Specimens ...
Read more