| Classification |
| |
AO Classification - 42
|
| Type A |
Simple fracture pattern |
| Type B |
Wedge fracture pattern
|
| Type C |
Comminuted fracture pattern |
|
| |
| Presentation |
- Symptoms
- pain, inability to bear weight
- Physical exam
- inspection and palpation
- contusions
- blisters
- open wounds
- compartments
- palpation
- passive motion of toes
- intracompartmental pressure measurement if indicated
- neurologic
- deep peroneal n.
- superficial peroneal n.
- sural n.
- tibial n.
- saphenous n.
- pulse
- dorsalis pedis
- posterior tibial
- be sure to check contralateral side
|
| Imaging |
- Radiographs
- recommended views
- AP
- lateral
- ipsilateral knee, tibia, and ankle
- findings
- proximal fracture extended, apex anterior, varus
- apex extended due to patellar tendon
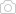
- varus due to pes anserinus + anterior compartment
- distal fragment flexed
- flexed due to hamstrings

- CT
- indications
- question of intra-articular fracture extension
|
| Treatment of Closed Tibia Fractures |
- Nonoperative
- closed reduction / cast immobilization
- indications
- closed low energy fractures with acceptable alignment
- < 5 degrees varus-valgus angulation
- < 10 degrees anterior/posterior angulation
- > 50% cortical apposition
- < 1 cm shortening
- < 10 degrees rotational alignment
- technique
- place in long leg cast and convert to functional brace at 4 weeks
- cast in 10 to 20 degrees of flexion
- outcomes
- rotational control is difficult to achieve by closed methods
- Operative
- external fixation
- indications
- fractures with extensive soft-tissue compromise

- polytrauma
- technique
- bi-planar and multiplanar pin fixators are useful
- intramedullary nailing
- indications
- enough proximal bone to accept two locking screws (5-6 cm)
- outcomes
- high rates of malunion with improper technique
- most common malunion
 
- valgus
- apex anterior (procurvatum)
- percutaneous locking plate

- indications
- inadequate proximal fixation for IM nailing
- best suited for transverse or oblique fractures
- minimal soft-tissue compromise
- technique
- may be used medially or laterally
- better soft tissue coverage laterally makes lateral plating safer
- outcomes
- lateral plating with medial comminution can lead to varus collapse
- long plates may place superficial peroneal nerve at risk

|
| Surgical Technique |
- Intramedullary nailing
- approach
- lateral parapatellar
- helps maintain reduction for proximal 1/3 fractures
- requires mobile patella
- medial parapatellar approach may lead to valgus deformity
- suprapatellar

- facilitates nailing in semiextended position

- starting point

- proximal to the anterior edge of the articular margin
- just medial to the lateral tibial spine
- use of a more lateral starting point may decrease valgus deformity

- use of a medial starting point may create valgus deformity

- fracture reduction techniques
- blocking (Poller) screws
      
- coronal blocking screw

- prevents apex anterior (procurvatum) deformity
- place in posterior half of proximal fragment

- sagittal blocking screw

- prevents valgus deformity
- place on lateral concave side of proximal fragment
- enhance construct stability if not removed

- unicortical plating
 
- short one-third tubular plate placed anteriorly, anteromedially, or posteromedially across fracture
- secure both proximally and distally with 2 unicortical screws
- universal distractor
- Schanz pins inserted from medial side, parallel to joint
- pin may additionally be used as blocking screws
- nail insertion
- options
- standard insertion with knee in flexion
- nail insertion in semiextended position

- may help to prevent apex anterior (procurvatum) deformity

- neutralizes deforming forces of extensor mechanism
- locking screws
- statically lock proximally and distally for rotational stability
- no indication for dynamic locking acutely
- must use at least two proximal locking screws
|
| Complications |
- Malunion
 
- incidence
- 20-60% rate of malunion following intramedullary nailing (valgus/procurvatum)
- treatment
- revision intramedullary nailing
- osteotomy if fracture has healed
- prevention
- blocking screws
- temporary plating
- universal distractors
- nailing in semiextended position
|