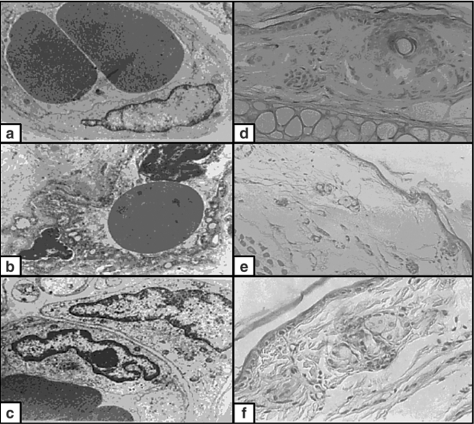
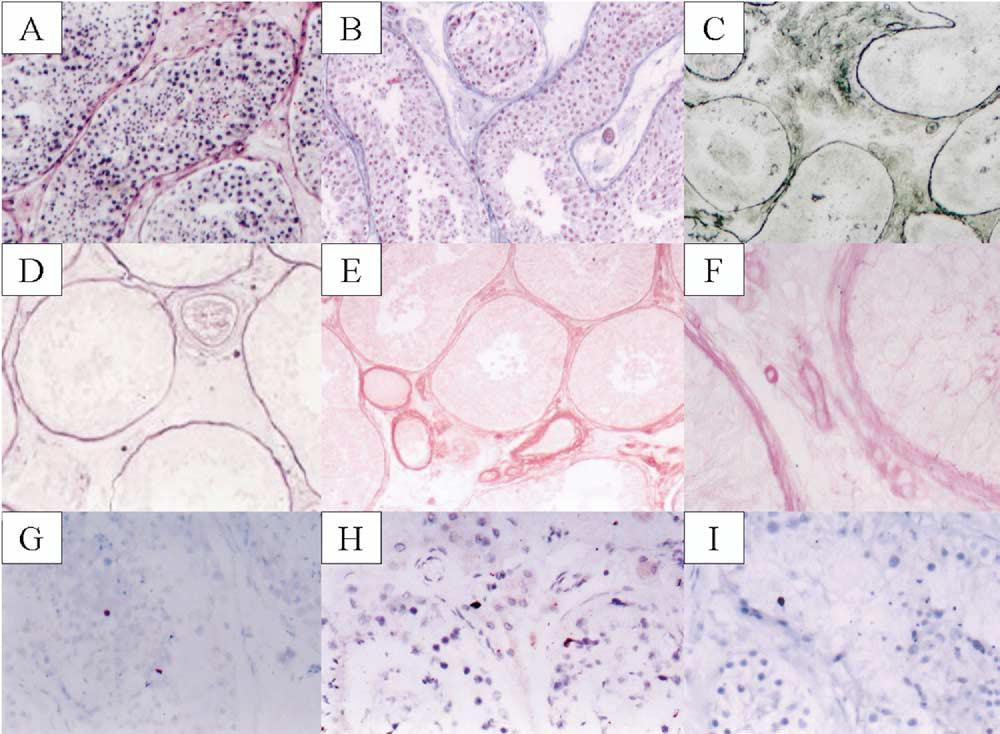
Comparative immunohistological and ultrastructural studies were performed on specimens taken before and after the application of chemical peels (Jessner’s solution and glycolic acid) and microdermabrasion to the clinically normal facial skin of the post-auricular region. Skin treated with chemical peels showed the immunohistological features of wound healing. Beside these, ultrastructural changes of cell injury were observed. These morphological changes were ...
Read more



.jpg)



.jpg)