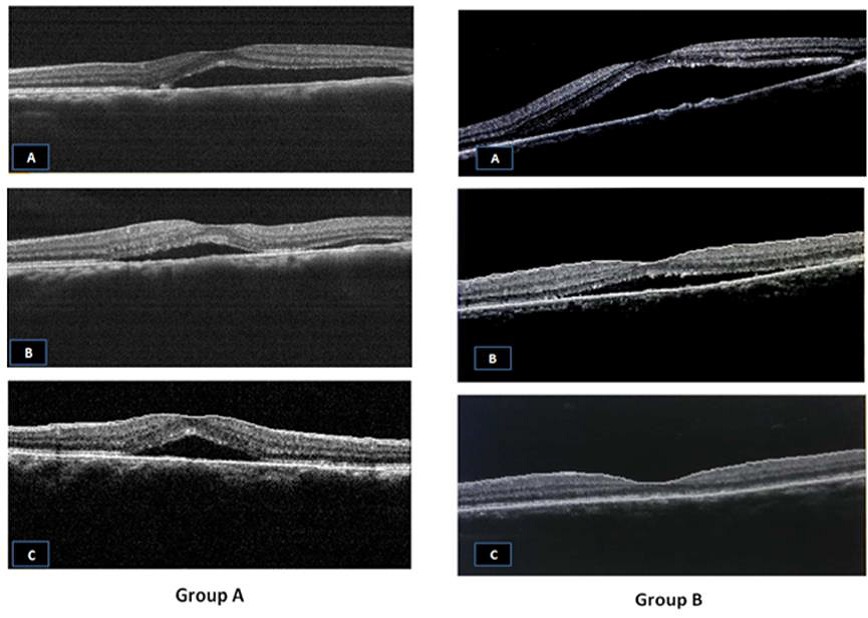
This study was designed to evaluate the efficacy of low-dose of oral acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) with focal argon laser for the treatment of acute central serous chorioretinopathy (CSCR). In this prospective case-control study, 40 Patients with acute CSCR were classified randomly to two groups; group A with no treatment as the control group and group B with argon Laser in focal treatment once, followed by aspirin, 100 mg per day orally, with follow up period of 12 months by evaluation of visual acuity, and by Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), every three months for one year. Patients in the second group treated with argon Laser and aspirin showed more clinically significant improvement in both visual acuity and OCT macular thickness by the end of the follow-up period when compared with the observational group. It was concluded that argon Laser with low-dose oral aspirin results in improvement of visual acuity and OCT macular thickness