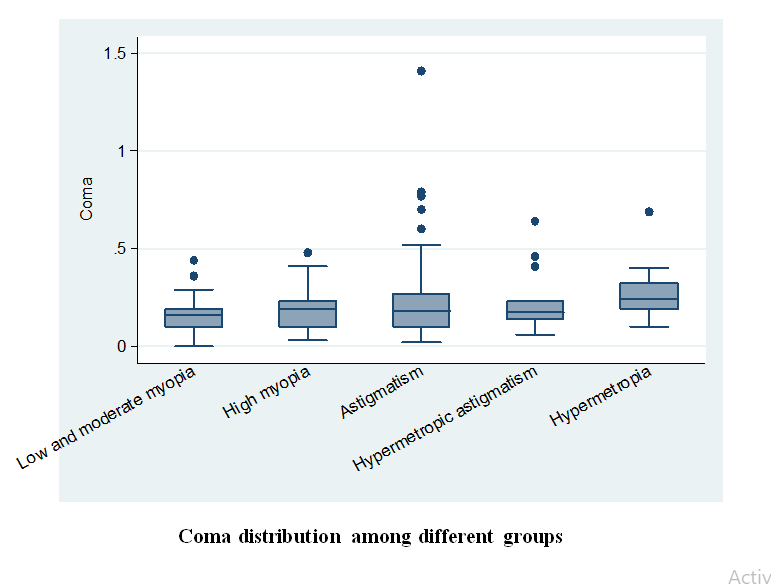
Purpose. To report the characteristics of anterior and posterior corneal high-order aberrations in patients with different refractive errors. Setting. This study was conducted at Sohag Refractive Center, Sohag, Egypt. Design. This is a retrospective observational study. Methods. This study evaluated 750 patients (750 eyes) who were seeking refractive surgery. The eyes were stratified into five groups (150 eyes/group) based on refractive error: mild-to-moderate myopia, high myopia, hyperopia, simple myopic astigmatism, and simple hypermetropic astigmatism. All patients were subjected to comprehensive ophthalmological examination including corneal topography and corneal aberrometry using the Scheimpflug–Placido topography (Sirius, CSO, Italy). Results. Coma aberration was statistically significant when compared in all five groups (). It was highest in the hypermetropia group (0.26 ± 0.12 μm) but lower in the moderate myopia, high myopia, myopic astigmatism, and hypermetropic astigmatism groups. Spherical aberration was lowest in the hypermetropia group and significantly different from that in the other groups. Trefoil was statistically insignificant when all groups were compared () but was highest in the myopic astigmatism group (0.24 ± 0.25 μm). Total RMS peaked in the hypermetropia group (0.99 ± 0.70). Conclusions. In normal corneas and regular refractive errors, the cornea-induced high-order aberration was minimal, and all types of refractive errors were associated with certain types of high-order aberrations, with a significant increase in spherical aberration in the hypermetropia group.