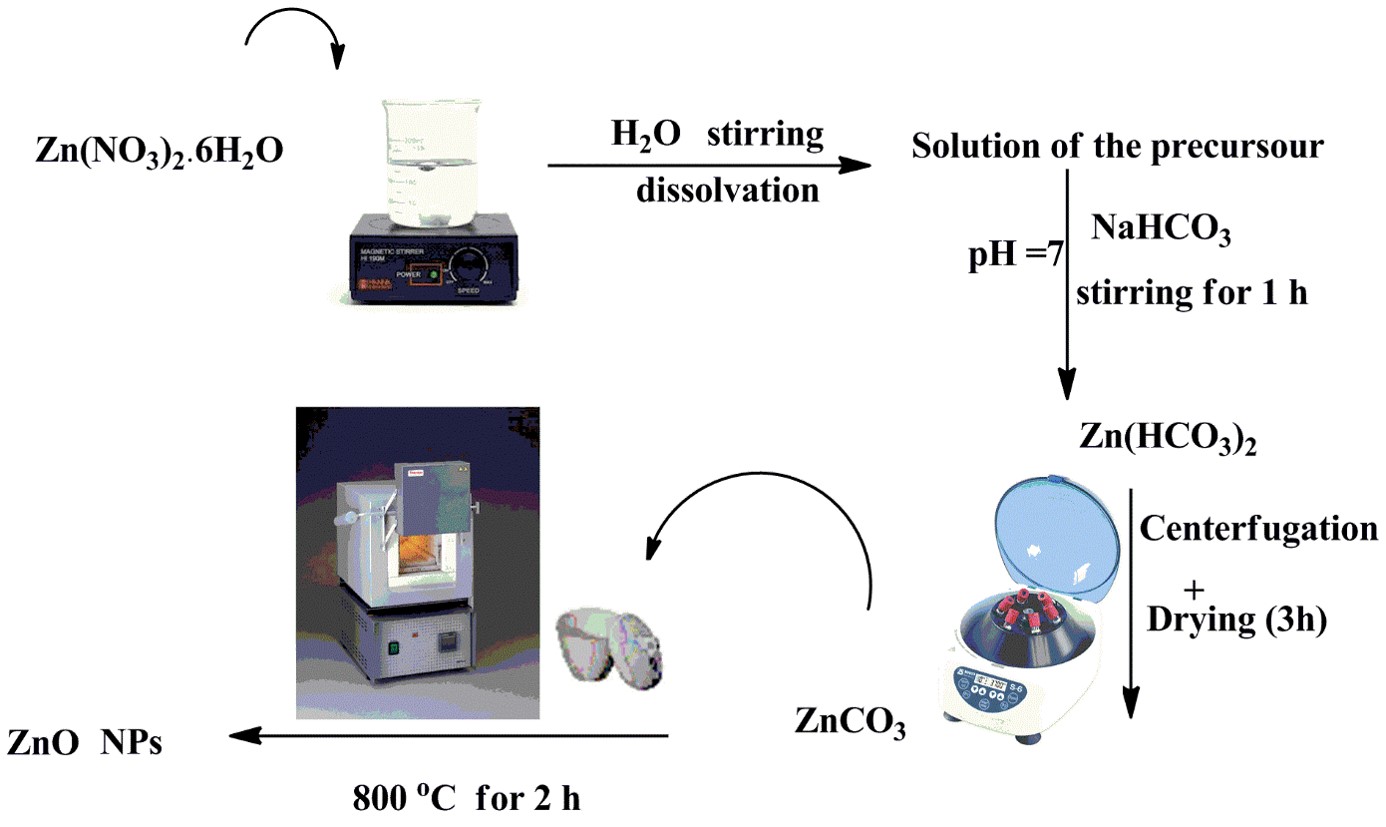
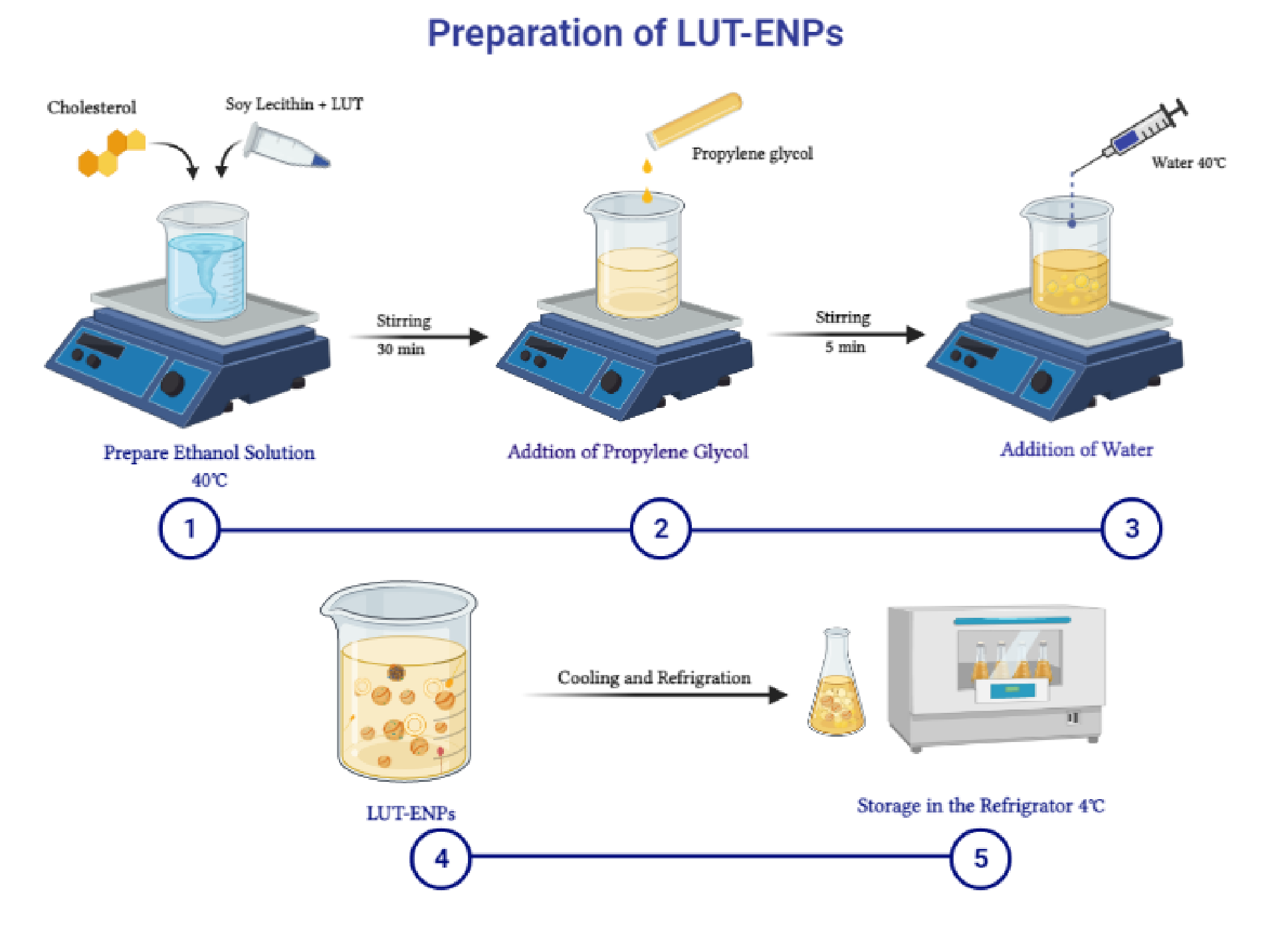
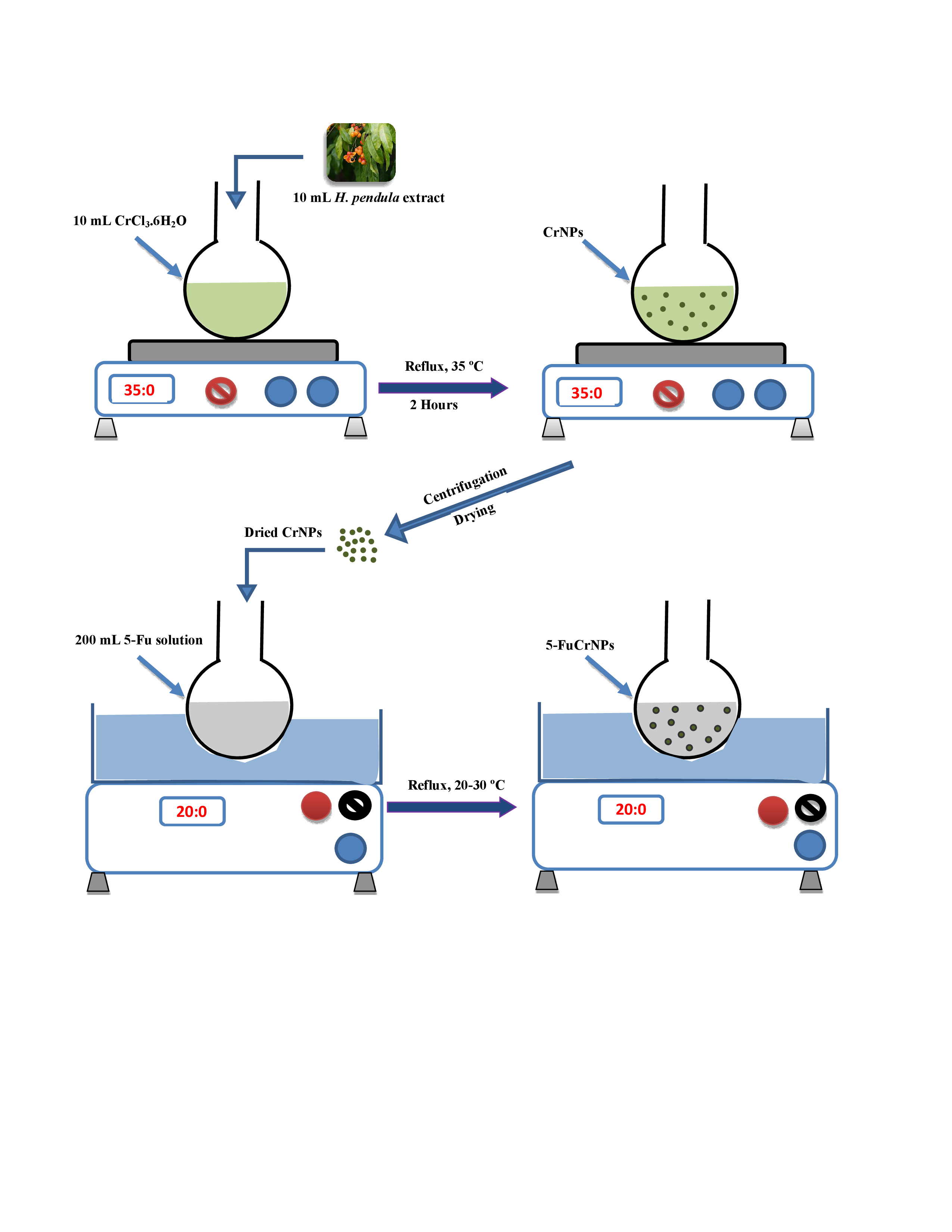
Skin is the largest mechanical barrier against invading pathogens. Following skin injury, the healing process immediately starts to regenerate the damaged tissues and to avoid complications that usually include colonization by pathogenic bacteria, leading to fever and sepsis, which further impairs and complicates the healing process. So, there is an urgent need to develop a novel pharmaceutical material that promotes ...
Read more