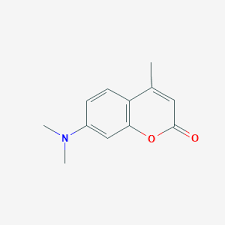
In the present study, reactivity base-catalyzed hydrolysis of 7-dimethylamino-4-methyl- 2H-chromen-2-one (DMAC) and 7-diethylamino-4-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one (DEAC) in binary aqueous–methanol and aqueous–acetone mixtures was examined at 298 K. Kinetic results, rate laws and reaction mechanisms were established. Moreover, the change in the activation energy barrier of the investigated compounds from water to water–methanol and water–acetone mixtures was estimated from the kinetic data. Base-catalyzed ...
Read more